What Your Scalloped Tongue Is Trying to Tell You About Your Health
Have you noticed wavy indentations along the edges of your tongue? This distinctive pattern, known as a scalloped tongue, might be your body’s way of signaling underlying health concerns. While the tongue impressions themselves rarely cause pain, they can point to conditions ranging from simple stress to serious medical issues that need attention.
What Exactly Is a Scalloped Tongue?
A scalloped tongue (also called crenated tongue, wavy tongue, pie crust tongue, or lingua indentata) features noticeable indentations or notches along its edges that create a rippled pattern resembling crimped pie crust edges. These markings form where your tongue presses against your teeth with enough force or frequency to leave lasting impressions.
The appearance varies from person to person – some may have slight, barely visible indentations while others display deep grooves that significantly change how the tongue looks. These indentations typically appear most prominently along the sides of the tongue where it contacts your teeth.
Try Our Dental Calculators
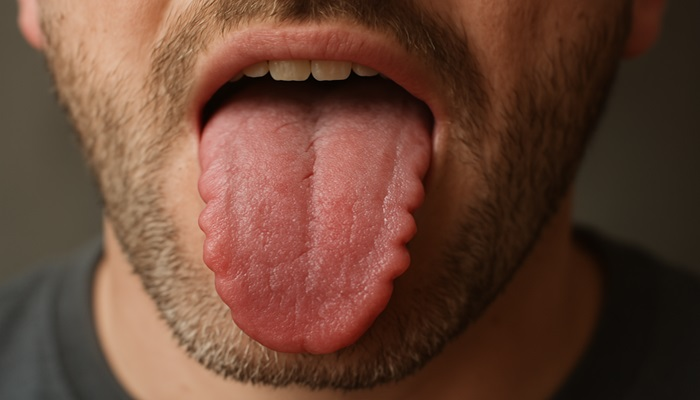

The normal, healthy tongue should have relatively smooth edges without significant indentations. When you see these wave-like patterns developing along the lateral borders that correspond to the placement of your teeth, it’s worth investigating the potential causes.
Why Your Tongue Develops These Wavy Patterns
Understanding what causes these distinctive marks can help you address potential underlying health issues. The development of a scalloped tongue can be attributed to numerous factors, many of which require different treatment approaches.
Physical Pressure Factors
Teeth Grinding and Clenching
Do you wake up with a sore jaw? Nighttime teeth grinding (bruxism) ranks among the most common causes of scalloped tongue. During sleep, the persistent pressure forces your tongue against your teeth, gradually creating those characteristic indentations.
A clinical study published in the National Medical Journal of India confirmed scalloped tongue as a finding in patients with nocturnal bruxism. The repeated pressure from grinding creates a pattern that matches your dental arch over time.
TMJ Disorders
When the temporomandibular joint connecting your jaw to your skull becomes misaligned, stuck, or fixed in problematic positions, it can alter your mouth structure, forcing your tongue into unnatural positions against your teeth. This abnormal pressure pattern often results in visible tongue scalloping over time.
TMJ disorders can cause multiple oral symptoms, including:
- Jaw pain or tenderness
- Difficulty chewing
- Clicking sounds when opening your mouth
- Locking of the joint, making it difficult to open or close your mouth
- Facial pain that radiates around the jaw area
Sleep-Related Connections
Sleep Apnea May Be Revealed By Your Tongue
Research has found a significant link between scalloped tongue and sleep disorders, particularly obstructive sleep apnea. During sleep apnea episodes, you may unconsciously press your tongue against your teeth to help maintain an open airway.
A 2017 study in the journal Acute Medicine & Surgery examining Japanese adults discovered that moderate-to-severe scalloped tongue was associated with a higher prevalence of nocturnal intermittent hypoxia, a marker for obstructive sleep apnea. This connection appeared even stronger in overweight individuals, with the study showing odds ratios of 2.83 and 4.74 for moderate-to-severe nocturnal intermittent hypoxia among overweight people with mild and moderate-to-severe scalloped tongue, respectively.
This significant correlation suggests your scalloped tongue could potentially serve as a clinical indicator when screening for sleep issues. If you have a scalloped tongue and experience any of these symptoms, consider discussing sleep apnea with your healthcare provider:
- Loud snoring
- Episodes of stopped breathing during sleep (often reported by another person)
- Gasping for air during sleep
- Morning headaches
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Difficulty concentrating during the day
- Irritability
- Waking with a dry mouth or sore throat
Nutritional Influences
Vitamin Deficiencies Show Up On Your Tongue
Your tongue can reveal when your body lacks essential nutrients. Deficiencies in B vitamins (particularly B12), riboflavin, niacin, and iron commonly contribute to tongue abnormalities, including scalloping.
When you lack these nutrients, your tongue may become inflamed and swollen, leading to scalloping as the enlarged tongue presses against your teeth. B12 deficiency specifically can cause not only tongue scalloping but also burning sensations, cognitive issues, neurological concerns, and persistent fatigue.
Common causes of B12 deficiency include:
- Vegetarian or vegan diets (B12 is primarily found in animal products)
- Regular antacid medication use (which can interfere with B12 absorption)
- Poor stomach acid production (necessary for B12 absorption)
- Conditions affecting the small intestine like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease
- Previous gastric bypass surgery
- Aging (older adults often have reduced ability to absorb B12)
Iron deficiency can also manifest with tongue changes, and often accompanies symptoms like:
- Unusual fatigue
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Cold hands and feet
- Brittle nails
- Dizziness
Medical Conditions That Affect Your Tongue
How Thyroid Problems Change Your Tongue
If your body produces insufficient thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism), you may experience general swelling throughout your body – including your tongue. This enlarged tongue (macroglossia) naturally develops scalloped edges as it presses against your teeth.
Additional symptoms that might appear alongside a scalloped tongue in hypothyroidism include:
- Hair loss, especially from the outer portion of eyebrows
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Muscle aches, tenderness, and stiffness
- Unusual bruising and slower wound healing
- Low blood pressure
- Elevated blood cholesterol levels
- Constipation
- Decreased sweating
- Heavier than normal menstrual periods
- Joint pain, stiffness, or swelling
- Depression
- Impaired memory
Protein Buildup Disorders
Amyloidosis, a condition involving abnormal protein buildup in organs and tissues (including the tongue), can cause tongue enlargement and subsequent scalloping. A case report in primary amyloidosis specifically noted scalloped tongue as a clinical finding. The accumulated proteins cause the tongue to swell, leading to scalloping when pressed against the teeth.
This serious condition can affect multiple organs, making early detection crucial. Other symptoms that might accompany the tongue changes include:
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Swelling in the ankles and legs
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
- Severe shortness of breath
- Difficulty swallowing
- An enlarged tongue that can interfere with speech and eating
Genetic and Congenital Conditions
Several genetic and congenital conditions can cause macroglossia (enlarged tongue) and subsequent scalloping, including:
- Down syndrome
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Apert syndrome
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Each of these conditions has unique characteristics, but tongue enlargement is a common feature that contributes to the development of scalloped edges.
Your Lifestyle Might Be Showing On Your Tongue
Dehydration Effects
Not drinking enough water leads to general tissue swelling as your body tries to retain fluids. Dehydration causes tissues to become puffy, which can result in your tongue pressing more firmly against your teeth, developing those characteristic scalloped edges.
Signs you might be dehydrated include:
- Thirst
- Dry or sticky mouth
- Reduced urine output
- Darker yellow urine
- Headache
- Muscle cramps
- Lack of energy
- Confusion or irritability
Stress and Anxiety Impact
High stress and anxiety levels often manifest physically through teeth clenching and jaw tension. These stress-induced behaviors put pressure on your tongue against your teeth, eventually creating visible indentations. Managing your stress can therefore play an important role in reducing tongue scalloping.
Chronic stress can also contribute to:
- Increased inflammation throughout the body
- Compromised immune function
- Changes in appetite and digestion
- Sleep disturbances
- Worsening of existing health conditions
Smoking’s Effect on Your Tongue
Tobacco use increases inflammation throughout the body and contributes to dehydration, both of which can promote tongue swelling and subsequent scalloping. Smoking also irritates the oral tissues directly, potentially exacerbating any existing inflammation or swelling. Additionally, smoking can mask symptoms of other conditions causing scalloped tongue, making diagnosis more challenging.
Recognizing Symptoms Beyond Scalloping
While the wavy tongue edges are the primary feature, several associated symptoms may occur depending on what’s causing the condition.
The scalloping itself typically doesn’t hurt, but you might experience:
- Persistent mouth or tongue soreness
- Speech or swallowing difficulties
- Numbness or tingling in your tongue
- Changes in how food tastes
- Accidentally biting your tongue more frequently when eating
- A feeling that your tongue is too large for your mouth
Additional symptoms that could help identify the underlying cause include:
- If sleep apnea is the culprit: Loud snoring, morning headaches, daytime fatigue, observed breathing pauses during sleep, waking up gasping for air
- With nutritional deficiencies: Fatigue, pale skin, mouth ulcers, dizziness, weakness, cognitive changes
- In hypothyroidism cases: Weight gain despite appetite changes, cold intolerance, constipation, dry skin, brittle nails, hair loss
- With TMJ disorders: Jaw pain, clicking sounds when opening your mouth, limited jaw movement, facial pain, headaches, earaches
How Your Healthcare Provider Will Diagnose the Cause
Proper diagnosis focuses not just on examining your tongue but identifying any underlying conditions that could be contributing to the scalloping.
What Happens During Evaluation
Your healthcare provider will typically:
- Perform a thorough visual examination of your tongue and mouth, looking for the characteristic indentations and assessing overall tongue size and appearance
- Ask about your medical history, including:
- Sleep patterns and potential sleep disorders (snoring, witnessed apneas, morning headaches)
- Teeth grinding or jaw clenching habits (do you wake with a sore jaw?)
- Diet and nutritional intake (particularly asking about B vitamin and iron sources)
- Existing health conditions (especially thyroid disorders)
- Current medications (some can contribute to tongue swelling)
- Stress levels and anxiety symptoms
- Alcohol consumption and tobacco use patterns
- Family history of relevant conditions
Diagnostic Tests You Might Need
Depending on what your provider suspects is causing your scalloped tongue, they may recommend:
- Blood tests to check nutritional levels (B12, folate, iron), thyroid function (TSH, T3, T4), and protein abnormalities
- Sleep studies like polysomnography if sleep apnea symptoms are present, which monitor your breathing patterns, oxygen levels, heart rate, and other vital signs during sleep
- Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to assess jaw structure or evaluate for conditions like amyloidosis
- Biopsy in rare cases if serious conditions like amyloidosis are suspected, which involves taking a small tissue sample for laboratory analysis
How You Can Address Your Scalloped Tongue
Treatment primarily focuses on addressing the underlying cause rather than treating the tongue indentations themselves. Once the root cause is properly managed, the scalloping often improves gradually over time.
Addressing Medical Contributors
For Sleep Disorders
If sleep apnea is diagnosed, your treatment might include:
- CPAP therapy: A machine that delivers continuous positive airway pressure to keep airways open during sleep, preventing the tongue from blocking the airway
- Oral appliances: Custom-fitted devices that help position your jaw to maintain an open airway during sleep
- Nasal dilators to improve airflow through the nasal passages
- Positional therapy: Training to avoid sleeping on your back, which can worsen apnea symptoms
- Lifestyle changes like weight loss, avoiding alcohol before bedtime, establishing regular sleep patterns, or adjusting sleeping positions
For Nutritional Gaps
When vitamin or mineral deficiencies are identified:
- Vitamin B12 supplements (oral pills, sublingual formulations, nasal gels, or in severe cases, injections), especially for vegetarians or those with absorption issues
- Iron supplements for those with iron deficiency, which come in various forms including ferrous sulfate, ferrous gluconate, and ferrous fumarate
- Dietary adjustments to increase foods rich in:
- B12 (meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, fortified plant milks and cereals)
- Iron (lean red meat, beans, spinach, dried fruits, iron-fortified cereals)
- Other B vitamins (whole grains, legumes, seeds, nuts, dark leafy greens)
For Thyroid Issues
If hypothyroidism is detected:
- Thyroid hormone replacement therapy with medications like levothyroxine (Synthroid, Levothroid) to normalize thyroid hormone levels
- Regular blood tests to monitor hormone levels and adjust medication dosages as needed
- Dietary considerations to support thyroid function (adequate iodine intake, selenium-rich foods)
- Avoidance of foods that can interfere with thyroid medication absorption (high-fiber foods, soy, walnuts, calcium supplements)
For TMJ Problems
When jaw issues contribute to tongue scalloping:
- Targeted jaw exercises to improve muscle function and jaw alignment
- Physical therapy with specialized TMJ therapists
- Dental interventions to correct bite problems or misalignments
- Anti-inflammatory medications or muscle relaxants for pain management
- Hot and cold therapy to reduce inflammation and pain
- Ultrasound or electrical stimulation treatments in physical therapy settings
Managing Physical Habits
For Teeth Grinding
To address habitual grinding and clenching:
- Custom-fitted night guards or mouth guards that provide a barrier between upper and lower teeth during sleep
- Bite splints designed specifically to reduce pressure from clenching
- Stress management techniques including meditation, biofeedback, or counseling to reduce the psychological factors contributing to bruxism
- Muscle relaxation exercises focusing on the jaw area before bedtime
- Avoiding stimulants like caffeine, especially in the evening
- Limiting alcohol consumption, which can worsen grinding behaviors
For Anxiety and Stress
When emotional factors contribute to tongue scalloping:
- Stress reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation
- Regular physical activity to reduce overall stress levels
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy to address underlying anxiety disorders
- Mindfulness practices to reduce tension in the jaw and facial muscles
- Anti-anxiety medications in some cases, as prescribed by a healthcare provider
- Improved sleep hygiene to reduce overall stress on the body
Lifestyle Changes That Help
Several general modifications can reduce tongue scalloping:
Hydration Improvements
- Drink adequate water throughout the day (aim for at least 8 glasses or 2 liters daily)
- Monitor urine color as an indicator of hydration status (pale yellow indicates proper hydration)
- Limit alcohol and caffeine which can contribute to dehydration
- Increase consumption of water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables
- Use humidifiers in dry environments to prevent moisture loss from breathing
- Track water intake using apps or marked water bottles if you struggle to stay hydrated
Dietary Adjustments
- Consume foods rich in B vitamins: eggs, fish, poultry, dairy, whole grains, dark leafy greens
- Increase iron intake: lean red meat, beans, spinach, dried fruits, fortified cereals
- Include anti-inflammatory foods: fatty fish, olive oil, nuts, fruits, vegetables
- Limit sugar and processed foods that may contribute to inflammation
- Consider food allergies or sensitivities that might be causing tongue inflammation
- Avoid irritating foods that may cause oral inflammation (spicy foods, acidic foods, alcohol)
Oral Hygiene Practices
- Regular brushing and flossing to maintain overall oral health
- Proper tongue cleaning as part of daily oral hygiene, using a tongue scraper or the edge of your toothbrush
- Routine dental check-ups to address any dental issues that might contribute to tongue scalloping
- Address any ill-fitting dental work that might be causing tongue positioning issues
- Maintain proper oral moisture with sugar-free gums or lozenges if dry mouth is an issue
Smoking Cessation
If you smoke, quitting can significantly improve oral health:
- Smoking cessation programs or aids like nicotine replacement therapy, prescription medications, or counseling
- Gradual reduction if quitting immediately is too challenging
- Support groups to help maintain motivation and provide strategies
- Alternative stress management techniques to replace the psychological aspects of smoking
- Regular dental cleanings to address existing tobacco stains and monitor oral health improvements
Quick Review
A scalloped tongue serves as a visible indicator of various underlying conditions ranging from simple habits like teeth grinding to serious medical issues like sleep apnea, nutrient deficiencies, or systemic diseases like hypothyroidism. While the indentations themselves rarely cause pain, they should prompt investigation into potential causes.
Effective management hinges on identifying and treating the underlying cause rather than focusing solely on the tongue’s appearance. Treatment approaches vary widely but may include dental interventions, nutritional supplementation, medication for underlying conditions, or lifestyle modifications addressing hydration, stress, and oral habits.
For most people, addressing the root cause leads to improvement or resolution of tongue scalloping over time. However, persistent or severe cases should always be evaluated by healthcare professionals to rule out serious conditions and ensure appropriate treatment.
When to see a doctor:
- If scalloping appears suddenly or is severe
- If you have other concerning symptoms alongside the scalloped tongue
- If the condition doesn’t improve despite addressing obvious potential causes
- If you experience pain, burning sensations, or difficulty with speech or swallowing
With proper diagnosis and targeted interventions, most cases of scalloped tongue can be effectively managed, improving both oral health and overall wellbeing.