Are you considering dental veneers to enhance your smile? Understanding the different types of veneers and their associated dental codes can help you make informed decisions about your treatment options and potential insurance coverage. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about dental veneer codes, procedures, and costs.
What Are Dental Veneers?
Dental veneers are thin shells of material that are bonded to the front surface of teeth to improve their appearance. They can address a variety of aesthetic concerns including:
- Discoloration
- Chips or fractures
- Minor misalignment
- Gaps between teeth
- Worn enamel
The Three Main Types of Veneers and Their CDT Codes
The American Dental Association (ADA) has established specific Current Dental Terminology (CDT) codes for different types of veneer procedures. These codes are essential for standardizing billing and insurance documentation.
Try Our Dental Calculators
D2960: Direct Resin Veneers (Chairside)
D2960 refers to chairside resin veneers that are applied directly to the teeth during a single visit. This procedure involves:
- Minimal tooth preparation
- Direct application of composite resin
- Sculpting and curing in one appointment
Benefits of Direct Resin Veneers:
- Cost-effective ($300-$600 per tooth)
- Preserves more natural tooth structure
- Completed in a single visit
- Easily repaired if damaged
Limitations:
- Less durable (5-7 year lifespan)
- Lower stain resistance
- Less dramatic aesthetic improvements
Direct resin veneers are ideal for patients with minor cosmetic concerns who prefer a more conservative approach.
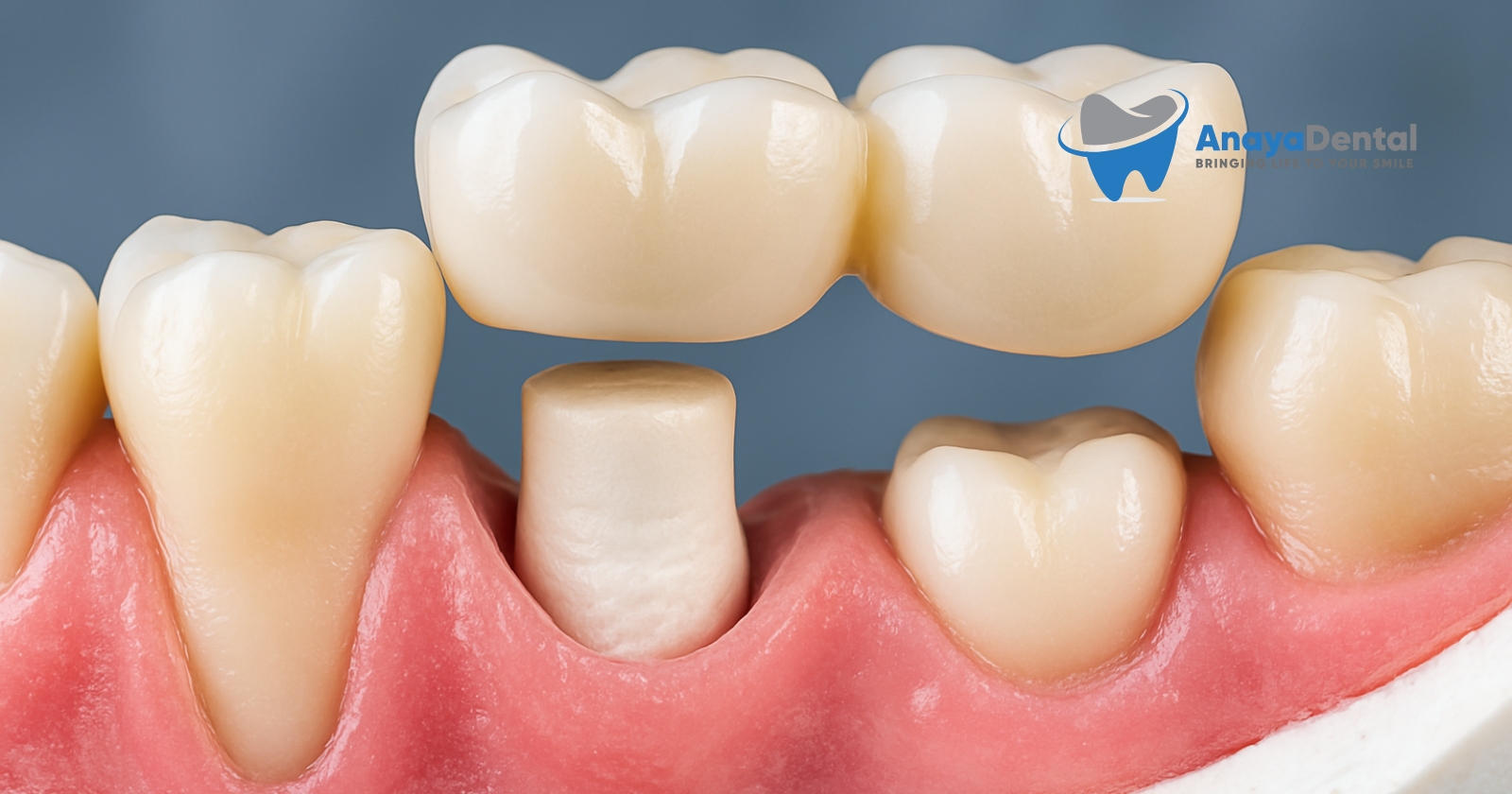
D2961: Indirect Resin Veneers (Lab-Fabricated)
D2961 covers laboratory-fabricated resin veneers, which require two separate appointments:
- First Visit: Tooth preparation and impression-taking
- Second Visit: Bonding the lab-created veneer
Benefits of Indirect Resin Veneers:
- Better customization for shape and color
- More durable than direct resin (7-10 year lifespan)
- Moderate stain resistance
- Excellent for multiple veneers
Cost Consideration: Expect to pay between $650-$1,500 per tooth, depending on your location and the complexity of your case.
D2962: Porcelain Veneers (Indirect)
D2962 designates porcelain laminate veneers, widely considered the gold standard in cosmetic dentistry.
Why Porcelain Veneers Stand Out:
- Superior light-reflective properties that mimic natural enamel
- Exceptional durability (10-15 year lifespan)
- Highest stain resistance
- Most natural-looking results
The Porcelain Veneer Process:
- Removal of 0.3-0.7mm of enamel
- Digital or traditional impressions
- Temporary veneers while awaiting lab fabrication
- Final bonding and adjustments
Investment: Porcelain veneers typically cost between $1,200-$1,700 per tooth, making them the most expensive option. However, their longevity often provides better long-term value.
Clinical Workflow for Getting Veneers
Initial Consultation and Planning
Before any veneer procedure begins, your dentist will conduct:
- Comprehensive oral examination
- Radiographs (X-rays)
- Intraoral scans
- Caries risk assessment (D0601-D0603)
Many dental offices now utilize digital imaging to create a smile simulation, allowing you to preview your potential results before committing to treatment.
Tooth Preparation and Temporary Solutions
For indirect veneers (D2961/D2962), your dentist will:
- Remove a small amount of enamel
- Take precise impressions
- Place temporary veneers while awaiting the final product
According to a 2024 study, 78% of patients report satisfaction with their temporary veneers during the waiting period.
Laboratory Fabrication and Final Placement
For indirect veneers, dental laboratories use your impressions to craft custom restorations. Advanced labs use specialized techniques to recreate the natural translucency of tooth enamel.
During the bonding appointment, your dentist will:
- Remove temporaries
- Clean the prepared teeth
- Etch the tooth surface
- Apply bonding agents
- Place and cure the veneers
Post-Treatment Care
To maintain your new veneers:
- Avoid highly staining foods and beverages
- Use non-abrasive toothpaste
- Wear a nightguard if you grind your teeth
- Schedule regular check-ups to monitor veneer integrity
Insurance and Cost Considerations
Will Insurance Cover My Veneers?
Most dental insurance plans classify veneers as cosmetic procedures and exclude coverage. However, exceptions exist when veneers are deemed medically necessary, such as:
- Restoring function to severely fractured teeth
- Addressing enamel loss due to acid erosion
- Replacing old restorations that have failed
Documentation is Key: If seeking insurance coverage, your dentist must provide comprehensive documentation linking the procedure to oral health outcomes.
Cost Variations by Region
Veneer pricing varies significantly based on location:
- Lower-cost regions (e.g., Memphis, TN): $650-$1,200 per veneer
- Higher-cost regions (e.g., San Francisco, CA): $1,500-$1,700 per veneer
Alternative Financing Options
If insurance won’t cover your veneers, consider:
- Dental savings plans
- Third-party financing options
- Practice-specific payment plans
- Bundle pricing for multiple veneers (can reduce per-unit costs by 15-20%)
Comparing Your Veneer Options
| Feature | Direct Resin (D2960) | Indirect Resin (D2961) | Porcelain (D2962) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | 5-7 years | 7-10 years | 10-15 years |
| Aesthetics | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Cost Range | $300-$600 | $650-$1,500 | $1,200-$1,700 |
| Enamel Removal | Minimal | Moderate | Significant |
| Stain Resistance | Low | Moderate | High |
| Visits Required | Single | Two or more | Two or more |
Ethical Considerations
The ADA emphasizes that proper coding must reflect diagnostic necessity rather than patient preference. Misrepresenting procedures through incorrect coding constitutes fraud and may trigger insurance audits.
Your dentist should:
- Accurately document your condition
- Take pre-operative photographs
- Provide written justification for treatment
- Use the appropriate CDT code for the selected material
Looking Ahead
As CAD/CAM technology continues to advance, we’re seeing improvements in veneer fabrication that may eventually reduce costs and increase accessibility. Digital workflows are streamlining the process and improving precision, which ultimately benefits patients seeking these transformative treatments.
Final Thoughts
Dental veneers offer versatile solutions for both aesthetic and functional concerns. While porcelain veneers (D2962) provide superior longevity and aesthetics, direct resin options (D2960) remain an excellent choice for minor corrections or patients with budget constraints.
By understanding the different CDT codes and their implications, you can have more productive conversations with your dentist and make informed decisions about your smile transformation journey.
Have you had experience with dental veneers? Which type worked best for you? Share your experiences in the comments below!